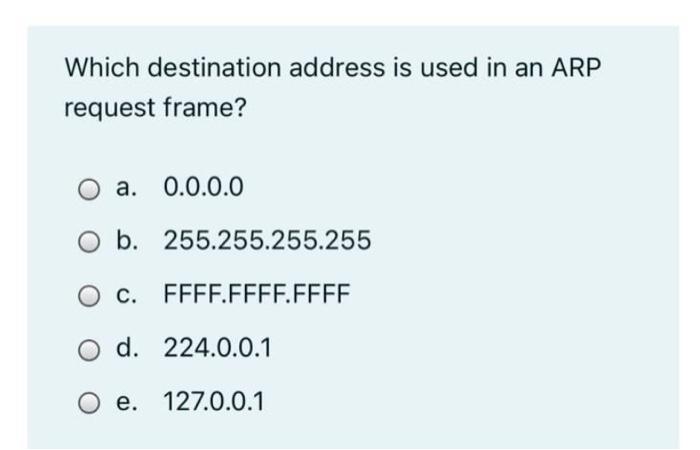
Which Destination Address is Used in an Arp Request Frame
A Destination MAC address a Source MAC address and an EtherType. A table is created by.
Arp Protocol Overview What Is Arp Arp Process Ipcisco
The ARP Request is an ARP payload carried within the appropriate L2 frame for the medium in use.

. It also checks whether the host is using the original IP address or a duplicate one. ARPRARP output shows the type of request and its arguments. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame.
The gratuitous ARP is used to update the ARP table of other devices. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all. Then leveraging the ARP table arp -a you can see all the devices that responded to that ping request.
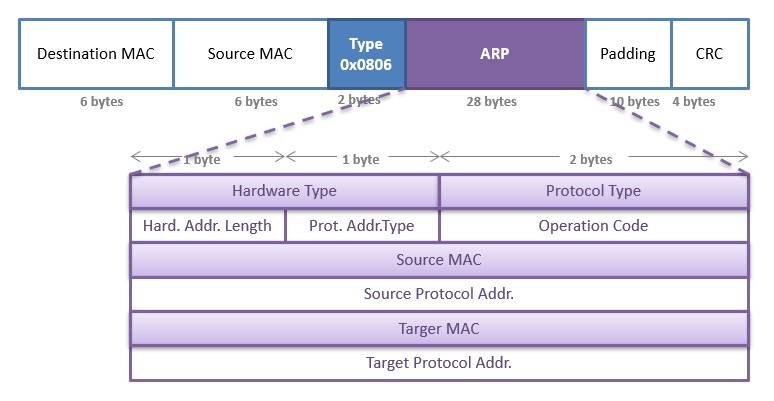
The Layer 3 device on the destination device network uses ARP to obtain the MAC address of the destination device and delivers the packet. The ARP request message has the following fields. The majority of the time this will be Ethernet which will also be the L2 medium we will be looking at in our examples.
First you can leverage the ping command to send out a ping request to a broadcast address. The author named it after the sound that sonar. The protocol field of the Ethernet frame can be used to denote the length of the header 80228023 networks.
The default is the broadcast address ffffffffffff. Both Source and Destination MAC. ARP IP destination address specification.
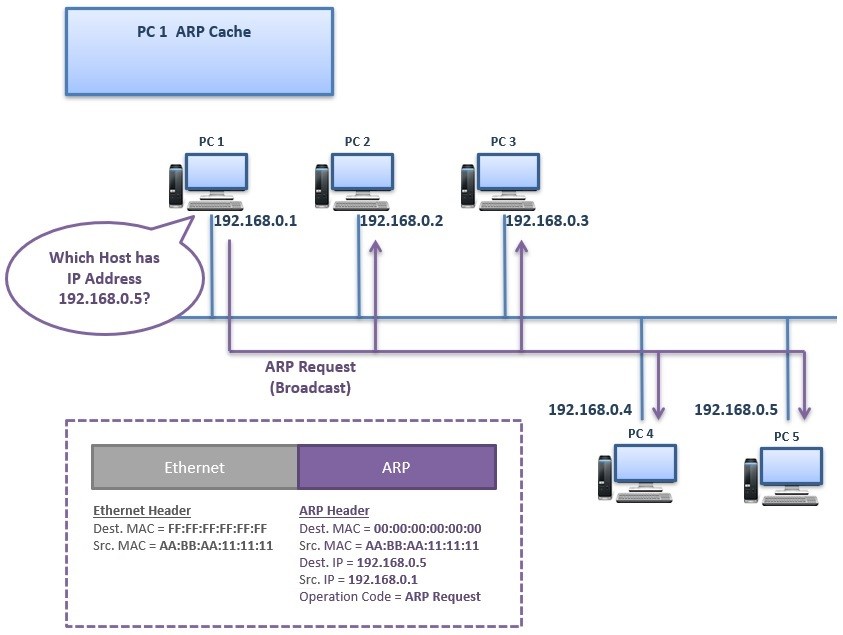
Since the ARP request is a broadcast it reaches all the nodes in the Subnet A which includes the e0 interface of the router but does not reach Host D. When sending a packet to a remote destination a host will need to send the packet to a gateway on the local subnet. The source device will not know the MAC address of the remote host.
The Source MAC Address and the Destination MAC Address are the most important part of an ethernet frame. The size of the ARP message depends on the upper layer and lower layer address sizes which are given by the type of networking protocol usually IPv4 in use and the type of hardware or virtual link layer that the upper layer protocol is running on. IP Interface Primary and Secondary Addressing.
Arp who-has csam tell rtsg arp reply csam is-at CSAM The first line says that rtsg sent an ARP packet asking for the Ethernet address of internet host. Switch will forward the frame out all interfaces except the incoming interface. ARP Reply will be a unicast to save Network Resources.
Most operating systems will also respond if the ARP request is sent to their MAC address or to a multicast address that they are listening on. The Ethernet header will include three fields. For example if you wanted to discover all the IPs connected to the 1921681024 network you can type.
Note that the ARP Reply has the Opcodef filled as 2 which is used to identify it as a ARP Reply. From the above introduction about both the layer switches an interesting question arises in our mind. The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address.
If the switches at the layer-2 dont follow any routing table then how they will learn the MAC address unique address of a machine like 3C-95-09-9C-21-G2 of the next hop. When the ARP message is not an ARP request or when the ARP request isnt for an IP address on an Ethernet network it is ignored by this target. The Address Resolution Protocol uses a simple message format containing one address resolution request or response.
Because the gateway will be the Layer 2 destination for the frame on this LAN segment the destination MAC address must be the address of. In order to find out the MAC address of host B host A sends an ARP request listing the host Bs IP address as the destination IP address and the MAC address of FFFFFFFFFFFF Ethernet broadcast. ARP Command is a TCPIP utility used for viewing and modifying the local Address Resolution Protocol ARP cache.
To explain the actual relationship between primary and secondary addresses we will run the following experiment. How to Use ARP. Here is a short sample taken from the start of an rlogin from host rtsg to host csam.
--destaddr or -T Send the packets to Ethernet MAC address This sets the 48-bit destination address in the Ethernet frame header. A frame is encapsulated with source and destination MAC addresses. Encapsulation of IP datagrams and ARP requests and replies on IEEE 802 networks other than Ethernet use Subnetwork Access Protocol SNAP.
ARP Address Resolution Protocol is a low level protocol working at Link layer level of the Internet Model or Internet protocol suite. --arp-mac-src address. When the computer with the IP Address 1921680122 receives the ARP Request it must prepare an ARP Reply and send back to the computer who sent the ARP Request.
The Source MAC Address is the MAC Address of the device that the ethernet frame is coming from. When using Nmap on a local network ARP protocol is applied by default for being faster and more reliable. Nping allows to generate packet under many protocols as it official website describes it can also be used for ARP poisoning Denial of.
It dynamically maps local DHCP or remote IP addresses when you configure frame relay. The router will respond with the MAC address of its interface the one which is connected to the same network as the. 0000 255255255255 FFFFFFFFFFFF AAAAAAAAAAAA the physical address of the destination host Answers Explanation Hints.
The format is intended to be self explanatory. The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address. The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN.
The Destination MAC Address is the MAC Address of the device which is going to receive the ethernet frame. It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address. Ip addr add 1011124 dev dummy.
Reverse ARP RARP - It is a networking protocol used by the client system in a local area network LAN to request its IPv4 address from the ARP gateway router table. Ip addr add 1011224 dev dummy. The answer is that it will do it by following the Address resolution Protocol.
When using inverse ARP we know the DLCI or remote router but dont know its IP address. The ping utility was written by Mike Muuss in December 1983 during his employment at the Ballistic Research Laboratory now the US Army Research LaboratoryA remark by David Mills on using ICMP echo packets for IP network diagnosis and measurements prompted Muuss to create the utility to troubleshoot network problems. Layer 2 broadcast means that frame will be sent to all hosts in the same layer 2 broadcast domain which includes the ether0 interface of the router but does not.
Now lets break this down a little bit to understand how the MAC address table is built and used by an Ethernet switch to help traffic move along the path to its destination. An ARP request will be sent by the source and will be responded to by the router. A MAC address table sometimes called a Content Addressable Memory CAM table is used on Ethernet switches to determine where to forward traffic on a LAN.
Tentative --- the address is not used because duplicate address detection is still not complete or has failed. MAC Address Tables.
Arp Protocol Overview What Is Arp Arp Process Ipcisco

Arp Address Resolution Protocol Explained
Solved Which Destination Address Is Used In An Arp Request Chegg Com

A Unicast Arp Request Networking Tales

Arp Reverse Arp Rarp Inverse Arp Inarp Proxy Arp And Gratuitous Arp Geeksforgeeks
0 Response to "Which Destination Address is Used in an Arp Request Frame"
Post a Comment